Topological control
Overview
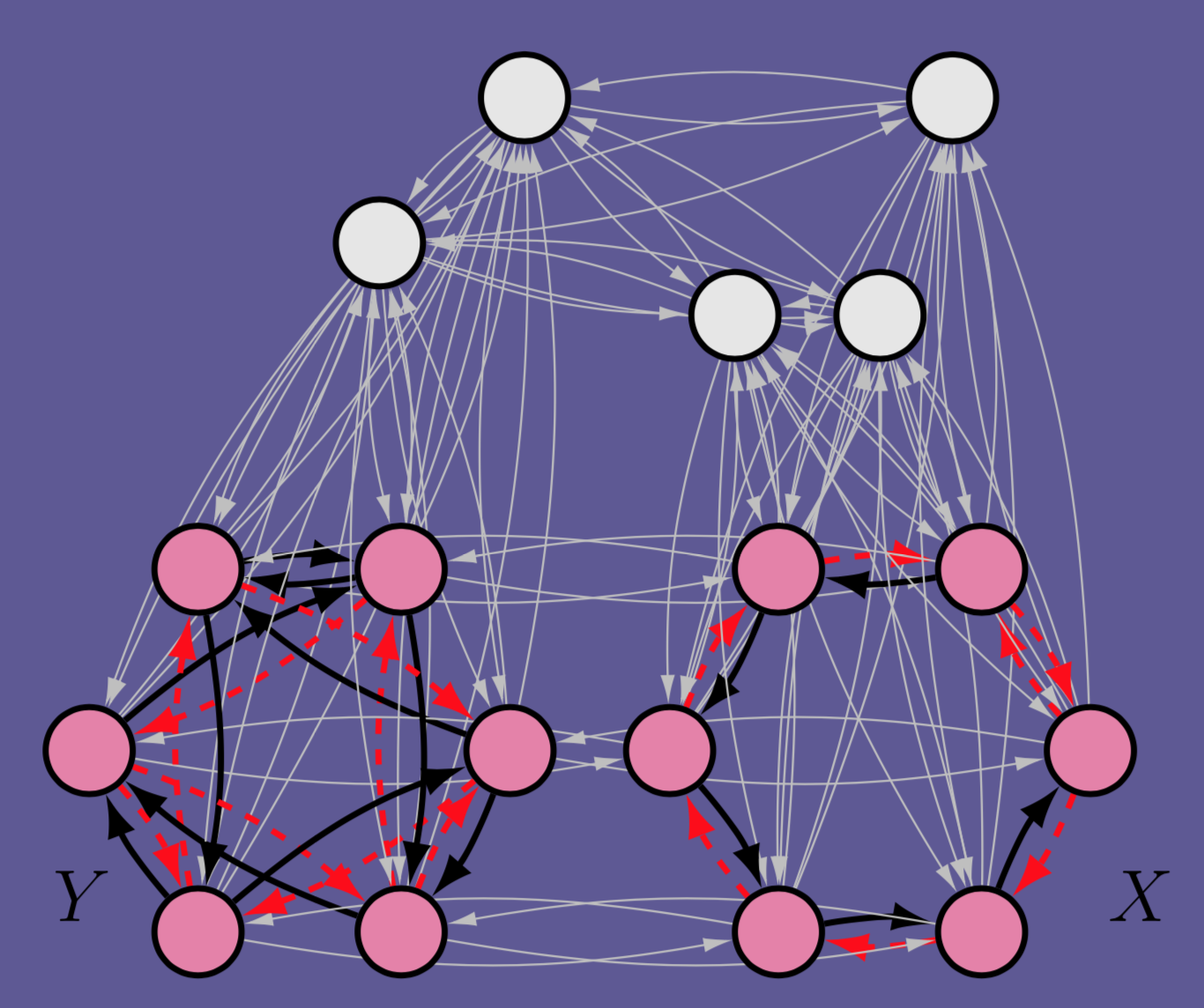
Different synchronization patterns are critical to the function of many interconnected systems (e.g., information processing in the brain). In practice, it is often important to be able to control these dynamical patterns without altering the node dynamics or imposing external control signal. In this work, we propose a new control strategy called topological control, which introduces minimal perturbations on the network structure so that the desired synchronization pattern can spontaneously emerge.
Abstract
Symmetries are ubiquitous in network systems and have profound impacts on the observable dynamics. At the most fundamental level, many synchronization patterns are induced by underlying network symmetry, and a high degree of symmetry is believed to enhance the stability of identical synchronization. Yet, here we show that the synchronizability of almost any symmetry cluster in a network of identical nodes can be enhanced precisely by breaking its structural symmetry. This counterintuitive effect holds for generic node dynamics and arbitrary network structure and is, moreover, robust against noise and imperfections typical of real systems, which we demonstrate by implementing a state-of-the-art optoelectronic experiment. These results lead to new possibilities for the topological control of synchronization patterns, which we substantiate by presenting an algorithm that optimizes the structure of individual clusters under various constraints.
Code
Our simulated annealing algorithm to improve the synchronizability of oscillator networks through minimal link rewiring, removal, or addition can be found here.
Press
- Scientists Discover Exotic New Patterns of Synchronization—Quanta Magazine
- The Math of How Crickets, Starlings, and Neurons Sync Up—Wired
References
- J. D. Hart*, Y. Zhang*, R. Roy, and A. E. Motter, Topological control of synchronization patterns: trading symmetry for stability, Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 058301 (2019)